This story was originally published by Mother Jones and is reproduced here as part of the Climate Desk collaboration.
The headline negotiations during the Paris climate summit in December were between national governments: What would China, the United States, and other big emitters be willing to do? But just outside the spotlight, some of the most optimistic commitments to curb greenhouse gas emissions, ramp up clean energy, and invest in adaptive measures were being made by cities.
A new analysis from social scientists at University College London sheds some new light on the money behind those municipal efforts — and the results paint a highly uneven picture. The researchers compared spending on climate adaptation in 10 major global cities — that is, investments in infrastructure, public health, water systems, etc., aimed at making them more resistant to climate change. All 10 cities are members of the Compact of Mayors, an initiative that came out of Paris to hold cities to a high standard of climate action.
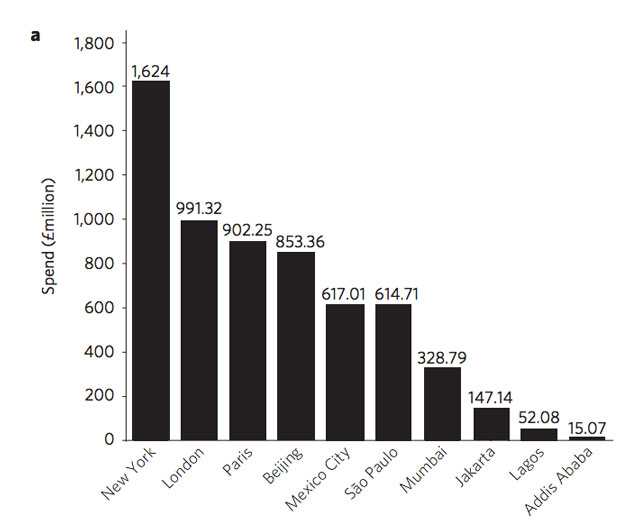
On average among those 10 cities, spending on climate adaptation accounted for one-fifth of one percent of GDP in 2015, or about $855 million. Not surprisingly, cities in wealthier countries such the U.S. and the U.K. spent far more than cities in African countries and Southeast Asia:
Nature
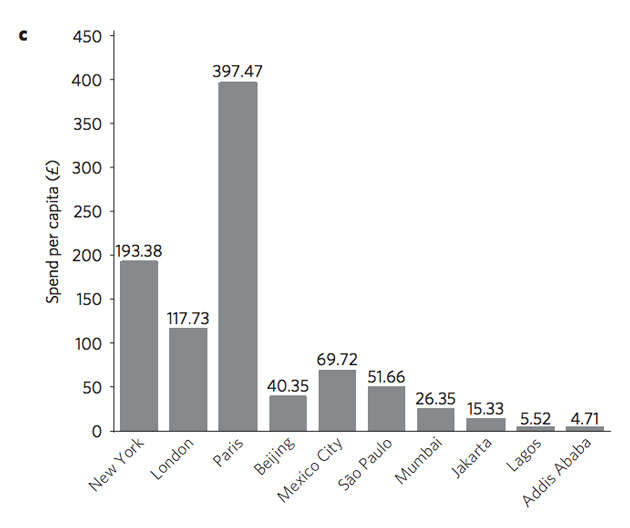
Cities in developing countries also lag behind on spending on a per-capita basis. (The Paris figure is so high in part because the study counted population just within a city’s official boundaries, not the surrounding metropolitan area, and Paris’ boundaries are relatively small) …
Nature
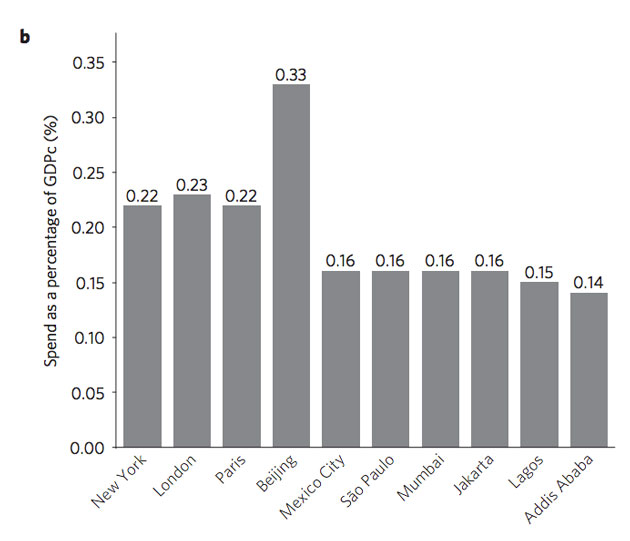
… and as a share of GDP:
Nature
The findings illustrate that spending on climate adaptation is more a function of wealth, and the value of local real estate, than the size of a city’s population or its relative vulnerability to climate impacts. The researchers conclude that “current adaptation activities are insufficient in major population centres in developing and emerging economies.”
That may not be very surprising — of course New York and London will be better able to rally funds for climate readiness than Addis Ababa. But it’s an important snapshot of the uphill battle developing countries face in confronting climate change.



