The headline at The Guardian says almost everything you need to know: U.S. carbon emissions fall to lowest levels since 1994.
Carbon dioxide emissions fell by 13% in the past five years, because of new energy-saving technologies and a doubling in the take-up of renewable energy, the report compiled by Bloomberg New Energy Finance for the Business Council for Sustainable Energy (BCSE) [PDF] said.
The reduction in climate pollution — even as Congress failed to act on climate change — brings America more than halfway towards Barack Obama’s target of cutting emissions by 17% from 2005 levels over the next decade, the Bloomberg analysts said.
By the end of last year, America’s emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gas emissions had fallen 10.7% from the 2005 baselines.
The caveat: The carbon emissions discussed are those related to energy production. Energy production isn’t all CO2 emission, but it’s a lot of it.
So here’s what that reduction looks like. Since 1974, levels of energy-related carbon emissions have seen two peaks. As indicated above, we’re on a downward trend, something David Roberts explained last year.
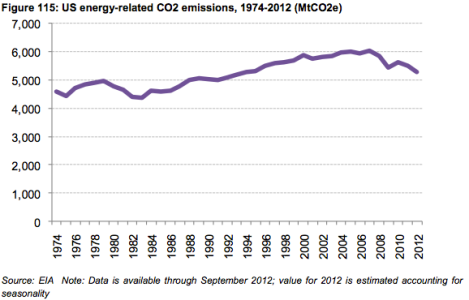
BCSEClick to embiggen.
Over the past few years, individual energy sources have played a fluctuating role in the reduction. In 2009, the collapsing economy meant lower emissions from all sources. That coal figure in 2012 is remarkable.
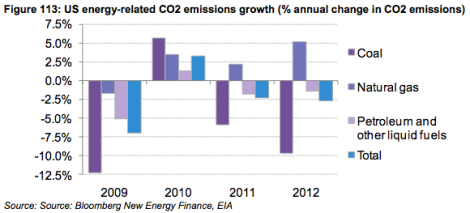
BCSEClick to embiggen.
This morning, the U.S. Energy Information Administration released state-by-state data on CO2 emissions through 2010. We put together this map showing net increase or reducton in CO2 emissions by state between 1994 and 2010. The darker brown a state is, the more its emissions rose; the darker green, the more emissions fell. Most states went up. But go Delaware!
[protected-iframe id=”22faa568995ba1f4d322c13d57fd7730-5104299-34907067″ info=”//ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/static/modules/gviz/1.0/chart.js” width=”470″ height=”350″]
The reduction — particularly the shift to renewables — is good news. Tempered with two caveats: This is only the United States. And the rate of decline is still far too low.



